Pointers In C
- Pointer are the variables which stores the address of another variable.
- It can only store address of variable only when their data types are same.
- For example:int type of pointer can only store address of integer type of variable.
- Float type of pointer can only store address of float type of variable And so on.
- let's declare some pointer variables.
Syntax:declaring pointer
datatype *pointer_variable_name
datatype *pointer_variable_name
Declaring : pointer variables
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int *i_p; //int type of pointer
//it can store address of integer variable.
float *f_p; //float type of variable
//it can store address of float variable.
char *c_p //char type of pointer
//it can store address of character variable.
}
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int *i_p; //int type of pointer //it can store address of integer variable. float *f_p; //float type of variable //it can store address of float variable. char *c_p //char type of pointer //it can store address of character variable. }
let's use above declare pointers.
Assigning: Address of int varaible to pointer variable
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i_var = 10; //integer variable.
int *i_p; //int type of pointer
//it can store address of integer variable.
i_p = &i_var; //assigning address of i_var variable
//to a pointer variable i_p.
}
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int i_var = 10; //integer variable. int *i_p; //int type of pointer //it can store address of integer variable. i_p = &i_var; //assigning address of i_var variable //to a pointer variable i_p. }
Lets understand visually.
Assigning: Address of float varaible to pointer variable
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
float f_var = 1.2; //float variable.
float *f_p; //float type of pointer
//it can store address of float variable.
f_p = &f_var; //assigning address of f_var variable
//to a pointer variable f_p.
}
#include<stdio.h> void main() { float f_var = 1.2; //float variable. float *f_p; //float type of pointer //it can store address of float variable. f_p = &f_var; //assigning address of f_var variable //to a pointer variable f_p. }
Lets understand visually.
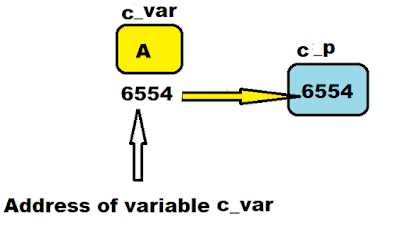
Assigning: Address of char variable to pointer variable
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char c_var = 'A'; //char variable.
char *c_p; //character type of pointer
//it can store address of char variable.
c_p = &c_var; //assigning address of c_var variable
//to a pointer variable c_p.
}
#include<stdio.h> void main() { char c_var = 'A'; //char variable. char *c_p; //character type of pointer //it can store address of char variable. c_p = &c_var; //assigning address of c_var variable //to a pointer variable c_p. }
Lets understand visually.
You can know the address of variable by Using & operator
let's use it.
Printing address
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i_var;//integer variable.
printf("%u",&i_var); //printing address
}
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int i_var;//integer variable. printf("%u",&i_var); //printing address }
Output:
655489.
- You can use %d specifier instead of %u but using %u specifier is good for printing Addresses of variables.
Accessing variables
- From pointer variable we can access the variable whose address is stored by pointer.
- It can done by using * Operator.
Syntax : Accessing variables from pointer variable
*pointer_name
*pointer_name
Lets Access the variable:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i_var = 10;
int acc_var;
int *i_p; //int type of pointer
//it can store address of integer variable.
i_p = &i_var;//assigning address of i_var variable
//to a pointer variable i_p.
acc_var = *i_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer
//to variable acc_var.
#include<stdio.h> void main() { int i_var = 10; int acc_var; int *i_p; //int type of pointer //it can store address of integer variable. i_p = &i_var;//assigning address of i_var variable //to a pointer variable i_p. acc_var = *i_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer //to variable acc_var.
let's print the accessed value:
printf("variable stored by pointer was %d", acc_var);
printf("variable stored by pointer was %d", acc_var);
Output:
variable stored by pointer was 10.
Let's see another example:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
float f_var = 1.2;
float acc_var;
float *f_p; //float type of pointer
//it can store address of float variable.
f_p = &f_var;//assigning address of f_var variable
//to a pointer variable f_p.
acc_var = *f_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer
//to variable acc_var.
#include<stdio.h> void main() { float f_var = 1.2; float acc_var; float *f_p; //float type of pointer //it can store address of float variable. f_p = &f_var;//assigning address of f_var variable //to a pointer variable f_p. acc_var = *f_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer //to variable acc_var.
let's print the accessed value:
printf("variable stored by pointer was %f", acc_var);
printf("variable stored by pointer was %f", acc_var);
Output:
variable stored by pointer was 1.2.
Let's Access character variable:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char c_var = 'A';
char acc_var;
char *c_p; //float type of pointer
//it can store address of char type variable.
c_p = &c_var;//assigning address of c_var variable
//to a pointer variable c_p.
acc_var = *c_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer
//to variable acc_var.
#include<stdio.h> void main() { char c_var = 'A'; char acc_var; char *c_p; //float type of pointer //it can store address of char type variable. c_p = &c_var;//assigning address of c_var variable //to a pointer variable c_p. acc_var = *c_p;//assigning accessed value from pointer //to variable acc_var.
let's print the accessed value:
printf("variable stored by pointer was %c", acc_var);
printf("variable stored by pointer was %c", acc_var);
Output:
variable stored by pointer was A.
- This how pointer works.
- This is a basics of pointers, So keep a good command on your basic , so you can easily understand advance concepts of Pointers
Further Concept:
- Array and Pointer
- What is array of pointer?
- how to initialize an array of pointers?
- How to Access elements of an Array Of Pointers?
- Functions and Pointers
- How to pass a Pointer To a Function?
- Call By reference
- How to declare Structure Pointer?
- Working with structure Pointer
- How to Create Structure Variable Dynamically ?
- Creating structure variable through malloc() and calloc()
Further Topics:
- How to initialize an structure variable?
- How to Access Structure member?
- What are Nested Structure?
- How to built an Nested Structure?
- How to Access members of Nested Structure?
- How to initialize Nested structure?
- Functions and Structure
- How to pass a structure variable to function?
- How to make function which will take structure variable as arguments?
- How to make function which will return structure variable?
- Array and Structure
- How to make array of structure variable?
- How to initialize array structure variable?
- How to Access members of an array of structure?
- How to take members of array structure as input from the user?
- Pointer and Structure
- How to Point a structure variable?
- How to declare a pointer of structure variable?
- How to Initialize an pointer of structure variable?
- How to access member of structure variable which is point by an pointer?
- What is '->' Operator?
- How to allocate memory for structure variable Dynamically
- How to allocate memory of structure variable using malloc() and calloc() function
- Self Referential Block
- What is Referential Structure?
- How to Create self Referential Structure?
- Applications of Self Referential Structures
- Practice Programs
People Also Searched:
- Functions In C
- Why Functions?
- What are Functions?
- how to write our functions?
- What are programmer define functions?
- How to declare function?
- How to define a function?
- What is function Prototype?
- how to declare a function?
- what are Actual Parameters?
- What are Formal Parameters?
- Function Call?
- how to call a Function?
- What are different types of calling function?
- Call by value
- call by reference
- Recursion
- Array and Functions
- How to pass an array to a function?
- What is Character array
- Functions for Characters
- Functions from #include<ctype.h> Header File
- what are isdigit(), islower() , isupper(),etc
- what are various string handling functions
- Functions from #include<string.h> Header File
- what are strcpy(), strcmp(), strncmp(), strcmpi(),etc
- strcmp() VS strncmp() VS strcmpi()
- Input And Output Functions
- How to take strings As Input
- What is gets() functions
- What is puts() function




0 Comments
Post a Comment